For those looking to break away from Microsoft’s constraints, switching to Linux could offer an exciting alternative. The Linux operating system has grown significantly, allowing many Windows applications and games to run smoothly, thanks to projects like Wine, Vulkan, and Proton.
Option 2: Switch to Linux – How to Get Started

Linux Mint
Linux is not a single operating system but a collection of various distributions, each with unique features and interfaces. Some of the popular distributions include Arch, Debian, Fedora, Manjaro, Mint, OpenSUSE, Red Hat, and Ubuntu. The variety can often overwhelm those new to Linux, leading to confusion or decision fatigue.
For users transitioning from Windows, Linux Mint is recommended due to its user-friendly graphical interface that resembles Windows, making it easier to adapt. Users can install it alongside Windows on a separate hard drive or SSD for easy switching.
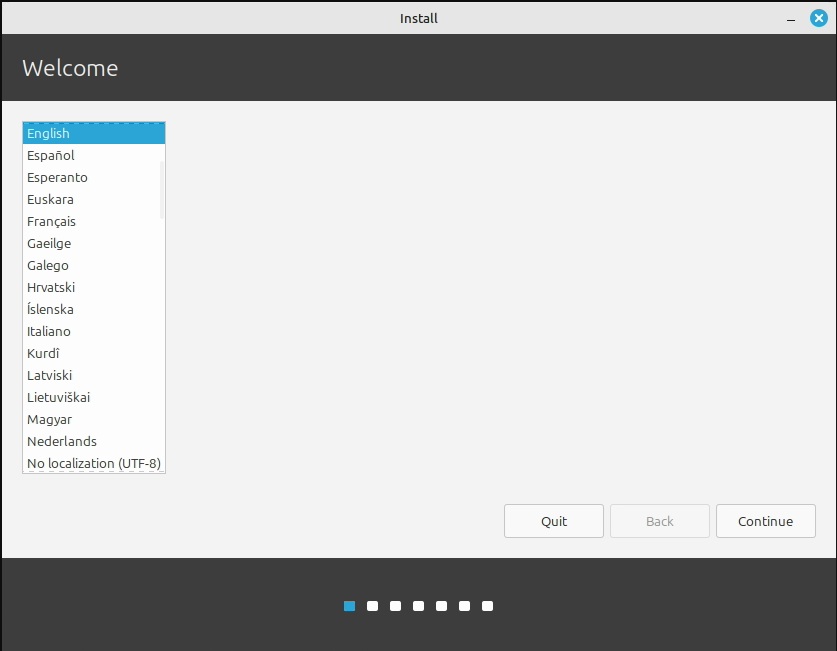
1. Download and Create Installation Drive
Begin by downloading the latest version of Linux Mint. Next, obtain the Balena Etcher application to create a bootable USB drive. Select the downloaded .iso file and a USB stick with at least 4GB of space, ensuring it contains no important files. Click Flash to overwrite the USB drive with the Mint installer.
Linux Mint
2. Start the Installation
After creating the installation media, restart your computer and access the start menu by pressing the appropriate key (usually Esc, F2, or F10) depending on your computer’s manufacturer. Select the USB stick when prompted, and wait for Mint to load.
Once loaded, double-click the Install Linux Mint icon. Follow the prompts to select your language and keyboard layout. It’s advisable to check the box for multimedia add-ons during installation.
When you reach disk formatting, choose Erase the disk and install Linux Mint. Select the appropriate drive for installation based on size. For instance, choose the smaller SSD if Windows is installed on a larger one. Click Install Now and continue. As the installation progresses, set your time zone, username, and password.
3. Getting Started with Linux Mint
After installation, restart your computer and log in to the Mint desktop. A welcome program will guide you through initial steps. The First Steps tab includes shortcuts to crucial features, like the Driver Manager for checking hardware drivers, particularly useful for Nvidia graphics card users.
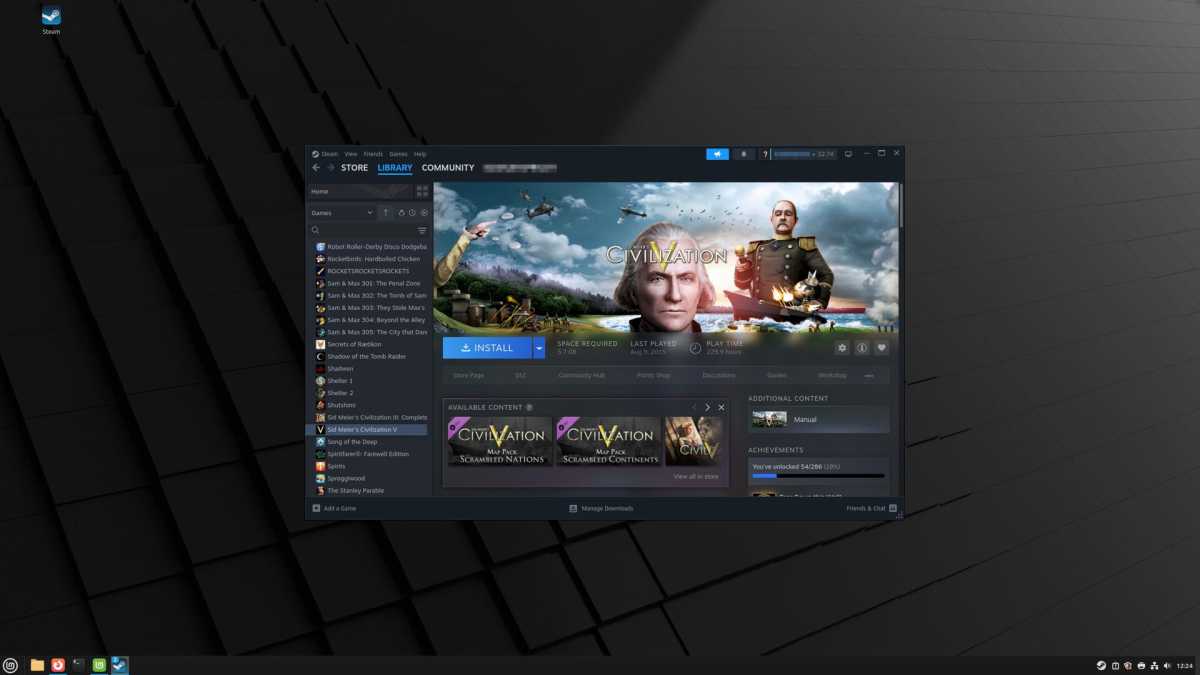
Software can be installed through the Software Manager, and system updates can be managed via Update Manager. For gamers, install Steam directly from the official Steam website, rather than through the application manager, to ensure better compatibility with most games.
Exploring the Mint interface should feel familiar to Windows users, allowing for an intuitive transition.
Foundry
If you encounter any issues, online resources and forums can provide assistance. Since Mint is based on Ubuntu, solutions for Ubuntu are typically applicable to Mint as well.
‘Linux Lite’ with Chrome OS
If delving into Linux seems daunting, consider using Chrome OS, which powers Chromebooks. While fundamentally based on Linux, it offers a simplified experience primarily through the Chrome browser.

